- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录39248 > LM3875T/NOPB (NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP) 56 W, 1 CHANNEL, AUDIO AMPLIFIER, PZFM11
Definition of Terms (Continued)
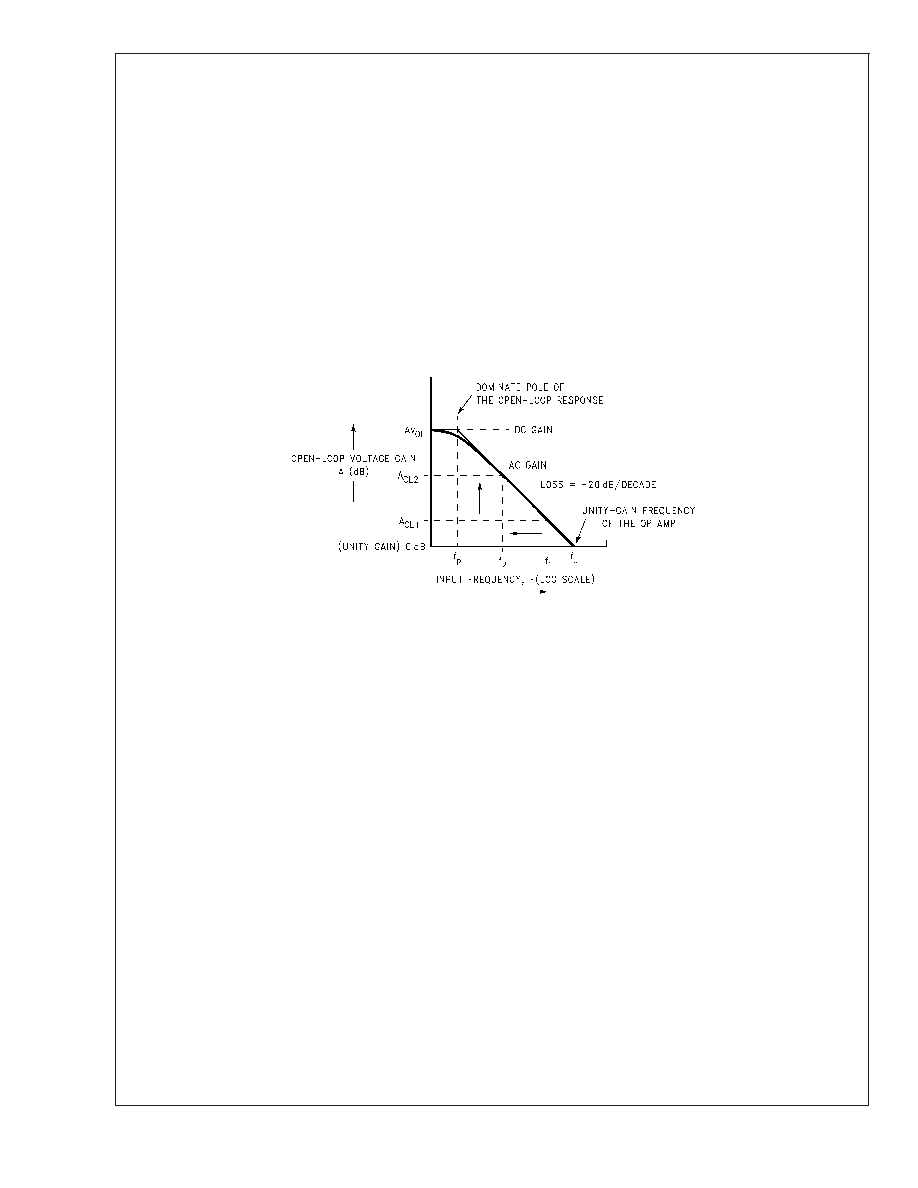
is also an excellent equation to determine the 3 dB point of a
closed-loop gain, assuming that you know the GBWP of the
device. Refer to the diagram below.
Bi-amplification: The technique of splitting the audio fre-
quency spectrum into two sections and using individual
power amplifiers to drive a separate woofer and tweeter.
Crossover frequencies for the amplifiers usually vary be-
tween 500 Hz and 1600 Hz. “Biamping” has the advantages
of allowing smaller power amps to produce a given sound
pressure level and reducing distortion effects produced by
overdrive in one part of the frequency spectrum affecting the
other part.
C.C.I.R./A.R.M.:
Literally: International
Radio
Consultative
Committee
Average Responding Meter
This refers to a weighted noise measurement for a Dolby B
type noise reduction system. A filter characteristic is used
that gives a closer correlation of the measurement with the
subjective annoyance of noise to the ear. Measurements
made with this filter cannot necessarily be related to un-
weighted noise measurements by some fixed conversion
factor since the answers obtained will depend on the spec-
trum of the noise source.
S.P.L.: Sound Pressure Level — usually measured with a
microphone/meter combination calibrated to a pressure level
of 0.0002 Bars (approximately the threshold hearing level).
S.P.L. = 20 Log 10P/0.0002 dB
Where P is the R.M.S sound pressure in microbars. (1 Bar =
1 atmosphere = 14.5 lb./in
2 = 194 dB S.P.L.).
01144914
FIGURE 3.
LM3875
www.national.com
18
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
LM399AH-20#TRPBF
1-OUTPUT TWO TERM VOLTAGE REFERENCE, 6.95 V, MBCY4
LM399AH-50#TR
1-OUTPUT TWO TERM VOLTAGE REFERENCE, 6.95 V, MBCY4
LM199AH#PBF
1-OUTPUT TWO TERM VOLTAGE REFERENCE, 6.95 V, MBCY4
LM399AH-50#PBF
1-OUTPUT TWO TERM VOLTAGE REFERENCE, 6.95 V, MBCY4
LM199AH-20#PBF
1-OUTPUT TWO TERM VOLTAGE REFERENCE, 6.95 V, MBCY4
LM199H#PBF
1-OUTPUT TWO TERM VOLTAGE REFERENCE, 6.95 V, MBCY4
LM199H#TRPBF
1-OUTPUT TWO TERM VOLTAGE REFERENCE, 6.95 V, MBCY4
LM399AH#TR
1-OUTPUT TWO TERM VOLTAGE REFERENCE, 6.95 V, MBCY4
相关代理商/技术参数
LM3875TF
功能描述:音频放大器 RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 产品:General Purpose Audio Amplifiers 输出类型:Digital 输出功率: THD + 噪声: 工作电源电压:3.3 V 电源电流: 最大功率耗散: 最大工作温度: 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:TQFP-64 封装:Reel
LM3875TF/NOPB
功能描述:音频放大器 RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 产品:General Purpose Audio Amplifiers 输出类型:Digital 输出功率: THD + 噪声: 工作电源电压:3.3 V 电源电流: 最大功率耗散: 最大工作温度: 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:TQFP-64 封装:Reel
LM3875TF/NOPB
制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:Audio Power Amplifier IC
LM3876
制造商:NSC 制造商全称:National Semiconductor 功能描述:Audio Power Amplifier Series High-Performance 56W Audio Power Amplifier w/Mute
LM3876_00
制造商:NSC 制造商全称:National Semiconductor 功能描述:Audio Power Amplifier Series High-Performance 56W Audio Power Amplifier w/Mute
LM3876CCT
制造商:未知厂家 制造商全称:未知厂家 功能描述:Single Audio Amplifier
LM3876T
功能描述:音频放大器 RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 产品:General Purpose Audio Amplifiers 输出类型:Digital 输出功率: THD + 噪声: 工作电源电压:3.3 V 电源电流: 最大功率耗散: 最大工作温度: 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:TQFP-64 封装:Reel
LM3876T
制造商:National Semiconductor Corporation 功能描述:56W W/Mute, 1 Channel Lm3876T IC Audio Amp